Tirzepatide: Understanding a Widely Discussed Option in Weight-Management Research

Interest in tirzepatide has increased significantly in recent years, particularly within clinical research and scientific discussions around metabolic health and weight management. Originally investigated in the context of type 2 diabetes, tirzepatide has since become the subject of broader research exploring its effects on appetite regulation, energy balance, and long-term metabolic outcomes. This article provides an educational overview of tirzepatide, how it is described in scientific literature, and why it continues to attract attention in ongoing research. It is not intended to promote use or replace professional medical guidance. What Is Tirzepatide? Tirzepatide is a synthetic peptide that acts as a dual agonist of the GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptors. These receptors are involved in metabolic signalling pathways that influence insulin secretion, appetite regulation, and glucose metabolism. Early development focused on glycaemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. Subsequent studies expanded investigation into its broader metabolic effects, including body-weight changes observed in controlled research settings. How Tirzepatide Is Described to Work in Research Settings In scientific literature, tirzepatide is commonly discussed in relation to its dual-pathway mechanism. By engaging both GIP and GLP-1 receptors, researchers examine its potential influence on: Appetite-related signalling Satiety and caloric intake Post-meal glucose responses Energy utilisation and metabolic efficiency Studies frequently highlight that dual-pathway compounds may produce different metabolic responses compared to single-pathway GLP-1 agonists, which has driven continued interest in comparative research. Overview of Clinical Research Findings Large-scale clinical trials have evaluated tirzepatide in controlled environments, reporting changes in body weight, metabolic markers, and glycaemic outcomes over extended study periods. For example, multi-phase trials such as the SURMOUNT programme explored weight-related outcomes alongside lifestyle interventions. These findings are often referenced in academic discussions as part of the evolving understanding of incretin-based therapies. It is important to note that clinical trial results reflect controlled conditions and may not directly translate to real-world use without appropriate medical oversight. Safety Considerations in Published Literature Scientific publications consistently emphasise that tirzepatide, like other incretin-based compounds, has been associated with gastrointestinal effects in some study participants, particularly during dose-escalation phases. Ongoing research continues to evaluate long-term safety, tolerability, and appropriate patient selection. Any discussion of side effects, suitability, or use should always be interpreted within the context of professional healthcare guidance and regulatory frameworks. Why Tirzepatide Remains a Focus of Ongoing Research Tirzepatide’s dual-receptor profile has positioned it as an important subject in broader metabolic research. Current and future studies are exploring: Long-term metabolic outcomes Durability of weight-related effects Cardiovascular and endocrine markers Comparisons with other incretin-based therapies As research continues, understanding of where tirzepatide fits within metabolic science is still evolving. Educational Resources and Further Reading Platforms such as TrimFast.net aim to provide educational content that helps readers understand how compounds like tirzepatide are discussed in scientific and clinical research contexts. Readers are encouraged to consult multiple reputable sources and qualified healthcare professionals when interpreting this information. Important Disclaimer This content is provided for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment recommendations. Tirzepatide is a prescription-only medicine in the UK and must only be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. Always consult an appropriate medical provider before making decisions related to medications or health conditions.
Tirzepatide Dosage Escalation: How It Works and Why It Matters

In clinical research and real-world medical practice, many treatments are introduced gradually rather than at full strength from the outset. This process—often referred to as dosage escalation or titration—is designed to help the body adapt while reducing the likelihood of unwanted effects. For medications and compounds studied in metabolic and appetite-related contexts, including tirzepatide, gradual dose adjustment is a commonly discussed approach in scientific literature. This article is intended for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. What Is Tirzepatide? Tirzepatide is a compound that has been studied for its activity at both GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptors. Because it acts on two pathways involved in glucose regulation and appetite signalling, it is often described in the literature as a dual-pathway agent. Research has explored tirzepatide in the context of metabolic health, including glucose regulation and body-weight-related outcomes. As with many compounds studied in this area, dosing strategies are a key focus of ongoing research. Why Gradual Dose Adjustment Is Discussed in Research Introducing higher amounts of a compound too quickly can increase the likelihood of gastrointestinal or tolerance-related effects. For this reason, gradual escalation is frequently referenced in clinical trial designs and prescribing information as a way to support tolerability. Rather than aiming for immediate effects, dose escalation prioritises: Allowing physiological systems time to adapt Monitoring individual response over time Reducing the likelihood of early discontinuation This approach reflects a broader principle used across many therapeutic areas—not just metabolic research. Typical Escalation Patterns Described in Literature In published studies and regulatory documentation, tirzepatide has often been evaluated using stepwise dose progression, with adjustments made at set intervals. While specific protocols vary depending on study design and patient population, escalation models commonly involve: An initial low-exposure phase Incremental increases at regular intervals Progression only if prior levels are well tolerated Importantly, not all individuals progress to higher levels, and many studies note that outcomes can be observed at different points along the escalation pathway. Any real-world dosing decisions must always be made by a qualified healthcare professional. Assessing Tolerability During Escalation Research highlights that tolerance can vary significantly between individuals. Factors often considered before escalation include: Overall comfort at the current level Presence or absence of gastrointestinal symptoms General wellbeing and day-to-day functioning Scientific discussions emphasise that escalation is not automatic, and remaining at a lower level for longer periods is sometimes appropriate. Commonly Reported Effects in Studies During dose-adjustment phases, studies have reported effects such as: Reduced appetite Changes in digestion or gastric emptying Transient gastrointestinal symptoms These observations are frequently described as dose-dependent and may lessen over time as the body adapts. Lifestyle factors—such as meal composition, hydration, and eating pace—are often noted in research discussions as variables that may influence overall tolerance. Why Escalation Is Viewed as a Long-Term Strategy Rather than focusing on speed, escalation strategies described in the literature are designed to support consistency and sustainability. A slower, monitored approach may help: Maintain adherence over longer periods Reduce interruption due to discomfort Align use with broader lifestyle and dietary considerations This long-view perspective reflects how metabolic research increasingly frames weight-related interventions—as part of an evolving, individualised process rather than a short-term fix. Final Thoughts Dosage escalation is a widely discussed concept in clinical research involving tirzepatide and similar compounds. Its purpose is not to accelerate outcomes, but to balance exposure, tolerability, and individual response over time. Educational resources like those provided by TrimFast aim to help readers better understand how these concepts are discussed in scientific and clinical contexts. Any decisions regarding use, dosing, or suitability should always be made in consultation with an appropriately qualified healthcare professional.
Tirzepatide Vial Sizes: Understanding 5mg & 10mg in Research Contexts
Tirzepatide Vial Sizes: Understanding 5 mg and 10 mg in Research Contexts Interest in tirzepatide has grown rapidly across clinical and scientific communities. Alongside this, questions often arise about the practical differences between lower- and higher-strength vials, particularly 5 mg and 10 mg formats. This article explores how different vial sizes are typically discussed in research, clinical development, and observational study settings, and why smaller quantities are commonly used during early stages of investigation. This content is provided for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or dosing advice. What Is Tirzepatide? Tirzepatide is a synthetic peptide investigated for its activity at both GIP and GLP-1 receptors. In scientific literature, it is studied for its role in metabolic signalling pathways related to insulin response, appetite regulation, and energy balance. It was initially developed for type 2 diabetes research and has since been evaluated in a wide range of controlled trials and real-world observational studies examining metabolic outcomes. Why Different Vial Sizes Exist In laboratory and clinical environments, multiple vial strengths are produced to support flexibility, precision, and staged evaluation. Smaller vial formats are commonly used during: Early-phase trials Dose-finding studies Tolerability and safety assessments Stepwise protocol designs Larger vial formats are more frequently associated with later-stage or continuation protocols, where parameters are already well established. 5 mg vs 10 mg Vials: Conceptual Differences 5 mg Vials Lower-quantity vials are often selected when: Initiating structured research protocols Conducting incremental evaluation Reducing material waste during early stages Supporting precision handling in laboratory environments They are commonly referenced in contexts where careful control and gradual adjustment are prioritised. 10 mg Vials Higher-quantity vials are typically referenced in: Extended research timelines Later-phase investigations Situations where handling efficiency is required Ongoing comparative or longitudinal studies They are not inherently “better” or “stronger” — they simply reflect different logistical and protocol needs. Why Smaller Quantities Are Often Used First Across clinical research more broadly, it is standard practice to begin with conservative quantities before progressing further. This approach supports: Improved data consistency Better monitoring of tolerability markers Reduced variability in early observations Alignment with ethical research frameworks This principle is not unique to tirzepatide and applies across many investigational compounds. Research-Focused Supply Considerations When sourcing peptide materials for scientific purposes, laboratories and research teams typically consider: Purity and batch traceability Storage stability Flexibility for protocol design Compliance with research-only use standards Vial size selection is therefore a practical decision, not a performance claim. A Note on Interpretation Discussion of vial formats should not be confused with recommendations for personal use. Any references to quantities or formats within scientific literature are context-specific and interpreted within controlled environments under professional oversight. Final Thoughts Understanding why different tirzepatide vial sizes exist helps clarify how research and development processes are structured. Smaller formats are commonly used during early or exploratory phases, while larger formats may support longer-term or later-stage work. As with all investigational materials, interpretation should remain grounded in published research, regulatory frameworks, and professional guidance.
Tirzepatide: 10 Key Considerations Before Use | Educational Guide

1. Tirzepatide Is a Prescription Medicine, Not a Supplement Tirzepatide is a once-weekly injectable medicine originally developed for the management of type 2 diabetes. It acts on two hormone pathways — GLP-1 and GIP — which are involved in insulin secretion, appetite signalling, and glucose control.It should not be confused with over-the-counter supplements or wellness products. 2. Its Effects Have Been Studied in Clinical Trials Tirzepatide has been evaluated in multiple large-scale clinical studies examining metabolic outcomes such as glycaemic control and body-weight changes. Reported outcomes vary by dose, duration, and individual factors, and results observed in trials may not reflect individual experiences. 3. Administration Is via Weekly Injection Tirzepatide is administered as a subcutaneous injection once per week. Individuals prescribed this medication are typically given instruction on correct handling and injection technique by a qualified healthcare professional. 4. Side Effects Can Occur, Particularly During Early Use As with many medicines affecting gastrointestinal and metabolic pathways, some people experience side effects, especially when first starting or adjusting dosage. These may include: Nausea Changes in bowel habits Reduced appetite Fatigue Side effects are not experienced by everyone and should always be discussed with a healthcare provider. 5. Lifestyle Factors Remain Important Medicines such as Tirzepatide are not considered standalone solutions. Clinical guidance consistently emphasises that nutrition, physical activity, and broader lifestyle factors remain relevant to overall health outcomes, regardless of medication use. 6. Use Is Typically Considered Over a Longer Timeframe Tirzepatide is not designed for short-term or occasional use. In clinical settings, it is usually discussed as part of a longer-term management approach, with regular review and monitoring by a healthcare professional. 7. Tirzepatide Is Not Suitable for Everyone There are known contraindications and precautions associated with Tirzepatide. Individuals with certain medical histories — including specific endocrine conditions or previous pancreatitis — may be advised not to use it. A full medical assessment is essential before initiation. 8. Treatment Commonly Starts at a Lower Dose To support tolerability, Tirzepatide is typically introduced at a lower dose before being increased gradually, depending on individual response. This stepwise approach is standard practice and aims to reduce the likelihood of adverse effects. 9. Ongoing Clinical Oversight Is Important Regular follow-up allows healthcare professionals to assess response, manage side effects, and determine whether continued use remains appropriate. Access to qualified guidance is considered an important part of responsible use. 10. Decisions Should Be Based on Informed Discussion Any decision involving prescription medicines should be made in consultation with a suitably qualified healthcare professional. Tirzepatide may be discussed as part of a broader conversation around metabolic health, risk factors, and individual circumstances. A Note on Information and Support At TrimFast, information is provided to help individuals better understand topics commonly discussed in clinical weight-management and metabolic health settings. Content is intended for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Disclaimer:This article is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before starting, stopping, or changing any medication.
Tirzepatide: Exploring Its Broader Role in Metabolic Health

Tirzepatide, also known by the brand name Mounjaro, was developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. In recent years, it has attracted wider clinical interest due to its effects on appetite regulation, glucose control, and overall metabolic function. Ongoing research continues to explore how these mechanisms may influence health outcomes beyond glycaemic management. Weight Regulation and Metabolic Function One of the most studied effects of Tirzepatide is its impact on body weight. By acting on both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, Tirzepatide influences appetite signalling and energy intake. Clinical studies have shown that participants using Tirzepatide alongside lifestyle changes experienced notable reductions in body weight over time. Importantly, weight reduction in a clinical setting is not solely about appearance. Maintaining a healthier weight is associated with a lower risk of conditions commonly linked to excess adiposity, including hypertension, dyslipidaemia, and impaired glucose tolerance. Cardiometabolic Considerations Research has also examined how Tirzepatide may affect markers related to cardiovascular and metabolic health. Improvements in blood glucose control and insulin sensitivity are well documented, and some studies have observed changes in lipid profiles and inflammatory markers. These findings are still being evaluated, and Tirzepatide is not currently authorised specifically for cardiovascular risk reduction. As with all prescription medicines, outcomes vary between individuals, and benefits observed in clinical trials may not apply universally. Beyond Blood Sugar Control While Tirzepatide’s primary indication remains the management of type 2 diabetes, its dual-receptor action has made it a subject of interest in broader metabolic research. Improved insulin sensitivity and appetite regulation may be relevant for individuals with obesity or features of metabolic syndrome, under appropriate medical supervision. It is important to note that Tirzepatide is not suitable for everyone, and treatment decisions should always be based on a full clinical assessment. A Medication Within a Wider Health Plan Tirzepatide is best understood as one component of a structured healthcare approach rather than a standalone solution. Diet, physical activity, and ongoing clinical monitoring remain central to long-term metabolic health. For those seeking factual information about Tirzepatide, its mechanism of action, and how it may be prescribed in a clinical setting, further educational resources are available through regulated healthcare providers.
Tirzepatide (Mounjaro): Understanding the Evidence Behind the Headlines

Tirzepatide, also known by the brand name Mounjaro, has received growing attention in recent months due to its role in the management of type 2 diabetes and its effects on body weight. Alongside scientific discussion, media coverage has sometimes raised concerns or highlighted isolated risks, making it important to understand what the evidence actually shows. This article explores how tirzepatide works, what clinical research tells us, and how to interpret public discussion in a balanced, evidence-led way. What Is Tirzepatide? Tirzepatide is a prescription medicine developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It acts on two hormone pathways involved in blood glucose regulation: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). By influencing these pathways, tirzepatide can: Support blood glucose control Affect appetite signalling Influence insulin sensitivity Its dual-receptor mechanism distinguishes it from earlier treatments that act on a single hormonal pathway. What Does Clinical Research Show? Tirzepatide has been evaluated in large, controlled clinical trial programmes involving adults with type 2 diabetes. These studies primarily assessed its effects on blood glucose control, with changes in body weight reported as secondary outcomes. Across trials, participants receiving tirzepatide experienced: Improvements in HbA1c levels Reductions in body weight over time It is important to note that results varied depending on dose, treatment duration, and individual patient factors. As with all prescription medicines, outcomes observed in clinical trials may not reflect real-world results for every person. Interpreting Media Coverage Some media reports have focused on potential risks, side effects, or the increasing interest in tirzepatide beyond its original licensed use. While scrutiny of new medicines is appropriate, headlines may not always reflect the full clinical context. Key points to consider: All prescription medicines carry potential side effects, which are assessed during regulatory approval Reported adverse effects must be weighed against documented benefits within approved use Regulatory authorities continue to monitor safety data after approval When evaluating media stories, it is advisable to rely on information from healthcare professionals and regulatory sources rather than isolated reports. Side Effects and Safety Considerations Like other medicines affecting GLP-1 pathways, tirzepatide may cause side effects, particularly during dose initiation or escalation. Commonly reported effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea or changes in bowel habits. For this reason: Treatment is typically started at a low dose Doses are increased gradually where appropriate Ongoing clinical oversight is recommended Tirzepatide may not be suitable for everyone, and a full medical assessment is essential before starting treatment. Availability and Demand Increased interest in newer metabolic treatments has led to periodic supply pressures globally. This reflects broader demand rather than a safety issue with the medicine itself. Healthcare providers may prioritise access based on clinical need, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Patients are encouraged to discuss availability and suitable alternatives with a qualified healthcare professional. A Broader Perspective on Metabolic Health Tirzepatide represents one of several modern approaches to managing type 2 diabetes and related metabolic conditions. While medication can play a role, it is typically used alongside lifestyle measures such as nutrition, physical activity, and long-term clinical monitoring. No single treatment is appropriate for everyone, and decisions should always be made on an individual basis. Final Thoughts Public discussion around medicines like tirzepatide can sometimes blur the line between evidence, expectation, and speculation. Understanding how the medication works, what clinical research demonstrates, and where its approved use sits helps create a clearer, more realistic picture. For individuals considering treatment, professional medical guidance remains the most reliable source of advice. This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Tirzepatide is a prescription-only medicine and should only be used under appropriate clinical supervision.
Exploring Tirzepatide: Benefits and Side Effects

Understanding Tirzepatide: Benefits, Considerations, and Side Effects Tirzepatide is a prescription medication used in the management of type 2 diabetes and, in some clinical settings, to support weight management under medical supervision. It works by activating two hormone pathways involved in blood glucose regulation and appetite signalling: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). Because of this dual mechanism, tirzepatide has attracted significant interest in metabolic health. As with any medicine, however, it is important to understand both its potential benefits and its possible side effects. Potential Benefits of Tirzepatide Blood Glucose RegulationTirzepatide supports blood sugar control by enhancing insulin release in response to raised glucose levels and reducing inappropriate glucagon secretion. This can help improve glycaemic stability in adults with type 2 diabetes when used as prescribed. Support for Weight ManagementSome individuals taking tirzepatide experience reductions in appetite and food intake. In clinical studies, these effects were associated with meaningful weight reduction over time when combined with dietary and lifestyle guidance. Results vary between individuals and depend on dose, duration, and adherence. Metabolic and Cardiovascular Risk FactorsResearch has also observed improvements in certain cardiometabolic markers, such as cholesterol levels and blood pressure, in some patients. These changes may be linked to overall metabolic improvements rather than a direct cardiovascular indication. Common Side Effects and Practical Considerations Like all prescription medicines, tirzepatide may cause side effects. These are often dose-related and most commonly occur when treatment is started or adjusted. Gastrointestinal SymptomsNausea, diarrhoea, constipation, or abdominal discomfort are among the most frequently reported effects. These symptoms are often temporary and may lessen as the body adapts. Gradual dose escalation under clinical guidance is commonly used to improve tolerability. Reduced AppetiteWhile appetite suppression may be part of the intended effect, it is important to maintain adequate nutrition. Monitoring food intake and focusing on nutrient-dense meals can help support overall health during treatment. Injection-Site ReactionsMild redness, swelling, or tenderness at the injection site can occur. Rotating injection sites and following proper injection technique can help reduce these reactions. Final Thoughts Tirzepatide is a clinically prescribed medication with a growing role in metabolic care. Understanding how it works, what effects to expect, and how side effects are commonly managed can help individuals make informed decisions in partnership with a healthcare professional. This information is intended for educational purposes only and does not replace personalised medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider to determine whether tirzepatide is appropriate for your individual health needs. Important Safety Information This content is provided for general informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Tirzepatide is a prescription-only medicine and should only be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional following an appropriate clinical assessment. Tirzepatide may not be suitable for everyone. It is not recommended for individuals with certain medical conditions, including a history of specific thyroid cancers, pancreatitis, or other endocrine disorders. As with all medicines, side effects may occur and individual responses can vary. Do not start, stop, or change any medication based on this information alone. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine whether this treatment is appropriate for you and to discuss potential risks, benefits, and alternative options.
Tirzepatide and Nutrition: How Essential Minerals Support Metabolic Health
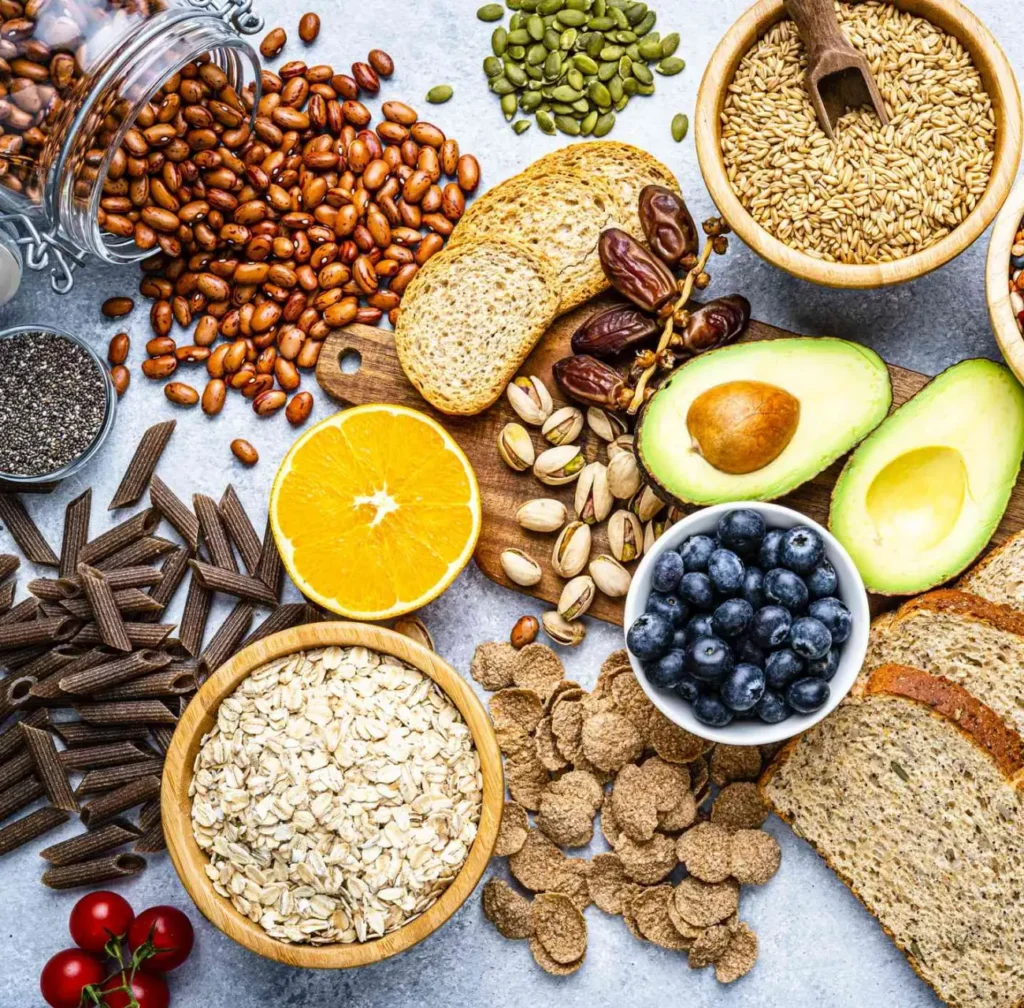

Tirzepatide is a dual-acting medication used in the management of blood glucose and body weight. While the medicine itself works through specific hormonal pathways, overall metabolic health is also influenced by broader lifestyle factors — including nutrition. A balanced diet that provides essential minerals plays an important role in supporting normal metabolic processes, insulin function, and energy regulation. Below, we explore several key minerals that are commonly discussed in relation to metabolic health and why maintaining adequate intake matters for people focusing on long-term wellbeing while using treatments such as tirzepatide. Magnesium and Metabolic Function Magnesium is involved in hundreds of enzymatic reactions in the body, including those linked to glucose metabolism and insulin signalling. Adequate magnesium intake is associated with normal muscle function, nerve signalling, and energy production. Low magnesium levels have been observed more frequently in people with metabolic conditions, which is why maintaining sufficient intake through diet is often recommended as part of general health guidance. Leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains are common dietary sources. Zinc and Normal Insulin Activity Zinc is an essential trace mineral required for immune health, cell growth, and hormone activity, including insulin storage and release. It contributes to normal carbohydrate metabolism and helps support pancreatic function. Ensuring adequate zinc intake as part of a varied diet may help maintain normal metabolic processes. Foods such as beans, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and shellfish naturally contain zinc. Chromium and Glucose Metabolism Chromium plays a role in the body’s ability to metabolise carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It contributes to normal blood glucose regulation by supporting insulin action at a cellular level. While chromium is needed only in small amounts, it is present in foods such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and lean meats. Meeting daily requirements supports overall nutritional balance rather than acting as a substitute for medical treatment. Calcium and Appetite Regulation Calcium is best known for its role in bone health, but it also contributes to muscle contraction, nerve signalling, and digestive enzyme function. Some research has explored calcium’s role in satiety and fat metabolism, although results vary. Including calcium-rich foods such as dairy products, fortified plant milks, and leafy greens supports general nutritional needs and long-term health. Potassium and Fluid Balance Potassium is essential for maintaining normal fluid balance, muscle function, and blood pressure. It also supports carbohydrate metabolism and cellular energy processes. Adequate potassium intake can be achieved through fruits and vegetables such as bananas, potatoes, spinach, beans, and avocados, forming part of a balanced diet. Nutrition as Part of a Broader Health Approach Tirzepatide works through well-defined pharmacological mechanisms. Nutrition does not replace or alter how the medication functions, but a well-balanced diet that includes essential minerals supports overall metabolic health and general wellbeing. At Trim Fast, we encourage a holistic approach that combines clinically guided treatment with practical lifestyle considerations such as nutrition, hydration, and sustainable habits — always under appropriate professional guidance. Important Information This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or nutritional advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making changes to your diet or starting supplements, particularly if you are using prescription medication. To learn more about tirzepatide and our clinically supported approach, visit TrimFast.net.
